
What Is LiDAR Technology?
Definition – What Is A LiDAR?
A LiDAR is an electronic component that is part of the family of sensors. More specifically, it belongs to the category of time of flight sensors (ToF). A sensor collects data on a physical parameter such as temperature, humidity, light, weight, distance, etc.
The acronym LiDAR stands for Light Detection And Ranging. It is a calculation method that determines the distance between the sensor and the target obstacle. A LiDAR uses a laser beam for detection, analysis, and monitoring.

Physical Phenomenon – How Does It Work?
LiDAR technology is a remote sensing technology that measures the distance between the sensor and a target. The light is emitted by the LiDAR and goes towards its target. It is reflected on its surface and returns to its source. As the speed of light is a constant value, LiDAR is able to calculate the distance between it and the target.
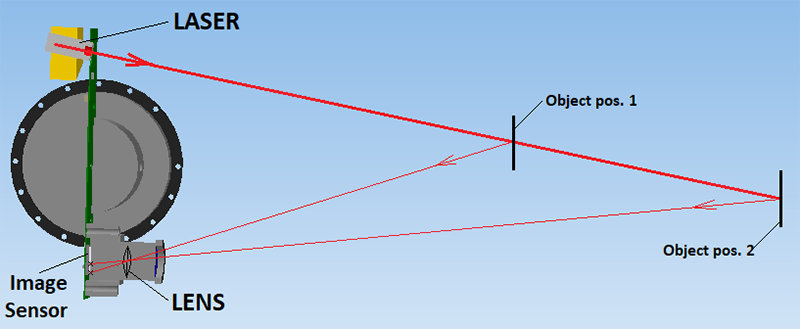
By knowing the position and orientation of the sensor, the XYZ coordinate of the reflecting surface can be calculated, represented by a point.
By repeating this process several times, the instrument establishes a complex “map” made up of all the points that LiDAR has collected.
The following diagram explains how a wave refracts on a surface. Part of the wave is reflected at the same angle of incidence (specular reflection), another part is refracted across the surface and the last part is diffusely reflected at different angles of incidence.
Overview Of LiDAR Features
Scanning Technology
This remote sensing technology can be used to measure the distance between the measuring instrument and an obstacle, in this case, we speak of a laser rangefinder. If the sensor scans to obtain the distances between the sensor and the surrounding obstacles, this is called LiDAR.
LiDAR rotates and measures the distance of obstacles over an angular range of up to 360 °, a complete circle. Its speed of rotation depends on the scanning frequency which is between 1 Hz and 100 Hz.
The Different Vision Systems Of LiDAR
There are three types of LiDAR: 1D, 2D or 3D. They work in the same way, the difference lies in the number of dimensions used.
For a 1D laser rangefinder, we need a single fixed laser beam that measures the distance between two points, the data obtained is on an axis and therefore a dimension.
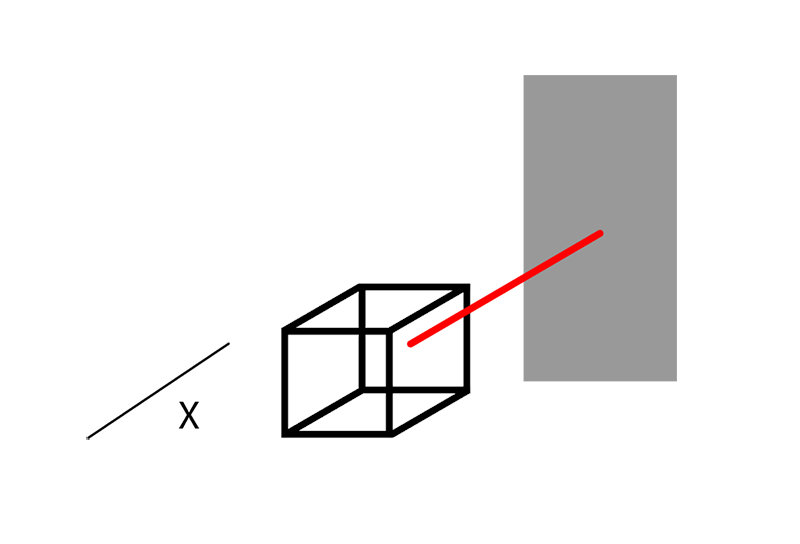
For a 2D LiDAR, only one laser beam is necessary. Indeed, it pulses according to a rotational movement on the horizontal plane and calculates the distance of the obstacles, we obtain data on the X and Y axes.
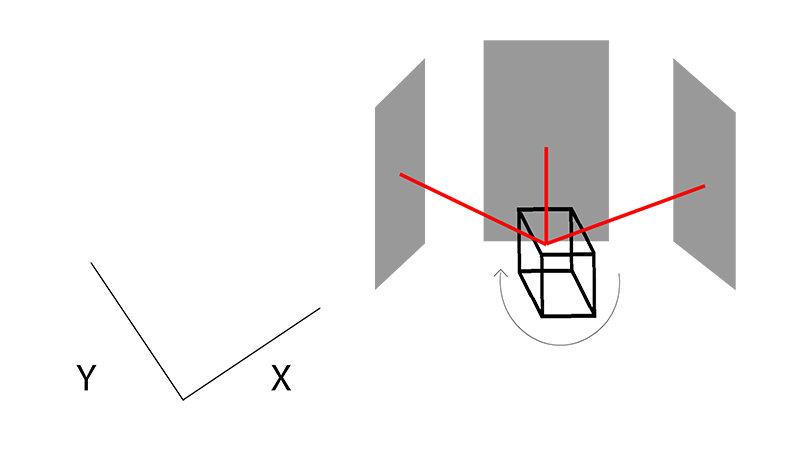
For a 3D LiDAR, the idea is the same, but there are several laser beams distributed on the vertical axis, always with this horizontal circular scan. We obtain data along three axes X, Y, and Z. Each laser beam will have an angle of difference delta with the other beams on the vertical plane.
Wave Length
The laser wavelength is an important parameter of LiDAR. Indeed, the sunlight received on the surface of the Earth is distributed over a wide spectrum of wavelengths:
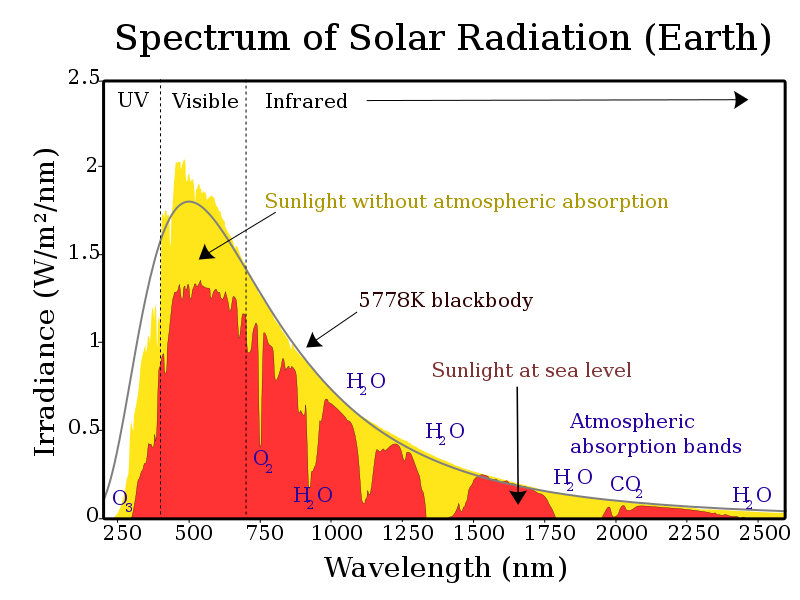
On this graph, some troughs stand out:
- 750 nm
- 940 nm
- 1125 nm
- 1400 nm
Laser beams more powerful than level 1 can be harmful to the human eye and damage the retina.
LiDARs use the following wavelengths:
- Infrared (1500-2000 nm) for meteorology / LiDAR Doppler – Scientific applications
- In the near-infrared (850 -940 nm) for terrestrial mapping
- Blue-red (500 -750 nm) for bathymetry
- Ultraviolet (250 nm) for meteorology
Interior Exterior
All LiDARs that comply with these technical standards can be used indoors. Only a few of them can be used outdoors depending on their characteristics. The following factors should be taken into account:
- Wavelength: at 500 nm, sunlight produces the highest level of disturbance
- Resistance to ambient light (in Lux): parameter which indicates the amount of light it can accept in order to function properly.
- The type of surface: transparent surface, smoke, fog, etc.
- Resistance to ambient noise: rain, snow, terrain, etc.
- The temperature range: temperature accepted for the proper functioning of the LiDAR
- Electromagnetic considerations: physical disturbances which can modify the behavior of the sensor
Outdoor LiDARs are more expensive due to their superior performance.
Distance
The range of LiDARs varies between 0.01m to 200m. Depending on the environment, the LiDAR will be exposed to artificial light, sunlight, terrain, transparent elements, etc. Choose a LiDAR with an appropriate distance. Indeed, in indoor use, a detection distance of up to 100m does not necessarily have much interest.
Fault
All LiDARs have two types of errors in their measurement:
Systematic error: this type of error displaces all the measures in a systematic and predictable way. Systematic errors cannot be eliminated, but their influence can be minimized.
Random error: additional errors, due to the environment and physical parameters (refractions, diffraction, etc.), can also occur. A random error occurs when the same exact measurements made by the LiDAR display different values.
The total error over the distance varies from ± 10mm to ± 200mm depending on the LiDARs.
Power Supply
All LiDARs require a power supply. Depending on the expected voltage and the current consumed by the components, the energy consumption or the power consumed can be calculated. When using a battery, this parameter has real importance, in fact, a LiDAR which consumes a lot of energy will shorten the battery cycle of the robot.
Performances
Angular range
This technical specification indicates the possible rotation range of the LiDAR.
For example, a LiDAR with an angular range of 360 ° can perform a full rotation (a full circle) during operation. If this parameter is less than 360 °, the LiDAR will only measure part of its environment, it will have a gray area at each scan cycle.
For a mobile robot, it is important to map all its environment, therefore a LiDAR which has an angular range of 360 ° will be a real asset.
Number of positions: step
This parameter indicates the number of positions at which the LiDAR measures during a scan cycle.
For example, a LiDAR with 1024 steps and an angular range of 360 ° will make a measurement for all the Angular range Pas = 360 ° 1024 = 0.35 °.
If the number of steps is too small, the robot will not have enough points to make a safe decision.
Angular resolution
The angular resolution is the result of the previous calculation (0.35 °), it indicates the precision of the LiDAR over its range of rotation. In this example, we will have a point every 0.35 °. Consequently, the smaller this number, the higher the quality of the ‘map’ generated. You should choose this parameter while knowing the necessary precision of the generated environment so that the robot can move there safely.
Scan frequency
This linear parameter indicates the speed of rotation of the LiDAR motor. Indeed, the scanning frequency indicates how many rotations the LiDAR is able to make in 1 second.
- Scan frequency: 1 Hz
- Angular velocity: 360 ° / second
- Rotation speed: 60 rpm (rpm)
For example, a LiDAR which has a scanning frequency of 10 Hz and an angular range of 360 ° will make 10 full rotations per second.
The choice of this parameter is essential when your robot moves quickly in its environment or when the environment moves quickly around the robot. No one likes to make a decision while lacking information.
Scan time
This parameter is: Scan time = 1 Scan frequency = x second / scan.
Points
It is the number of points measured. For a LiDAR with a laser beam, the number of points per scan is equal to the number of steps.
For example, 1024 points/scan means that a LiDAR with a laser beam will have 1024 points or samples in a scan cycle.
Sampling frequency
It is the number of points detected during one second.
For example, a LiDAR with an angular range of 360 °, 1024 steps, and a scanning frequency of 10Hz, the sampling frequency is 1024 * 10 = 10240 points/second.
You can improve one of two parameters (the step or the scanning frequency) to increase the amount of data received in one second.
Communication Interface
The interface, the controller and the communication protocol that will be used with the LiDAR must be able to follow the measurement of the data rate (I2C, PWM, SPI, serial, etc.), so as not to lose any information.
An essential element is to have the same data transmission speed (baud rate) between the LiDAR and the PC or the on-board card. If this speed is too low, the behavior will not correspond to that expected.
ROS
The Robot Operating System (ROS) is a collection of software libraries and tools designed to assist in the creation of robotic applications. From pilots to cutting-edge algorithms and powerful development tools, ROS is now an industry standard for any robotic project. It is an open-source solution.
The LiDARs presented on the Génération Robots site are all ROS compatible. Do not hesitate to consult our selection of LiDARs or to contact us, if you need more information on this technology.
Conclusion – Advantages And Disadvantages Of LiDAR
Benefits Of LiDAR
- Data can be collected quickly and with great precision
- LiDAR can easily be integrated with other sensors: sonar, camera, IMU, GPS, ToF sensors
- LiDAR technology can be used in daylight or in the dark, thanks to an active light sensor
- Can be used to collect data on places inaccessible to humans
- LiDARs are fast and very precise. It is a great tool for collecting data over large tracts of land
- Once properly configured, a LiDAR is a stand-alone technology and can operate on its own.
Disadvantages Of LiDAR
- LiDAR can be expensive depending on the specifications required by your project
- LiDARs are ineffective in heavy rain, low clouds, fog or smoke, or in the presence of transparent obstacles
- Analyzing the huge amount of data collected can take time and resources
- The powerful laser beams used in some LiDARs can damage the human eye
- It is difficult to penetrate very dense material